Zip
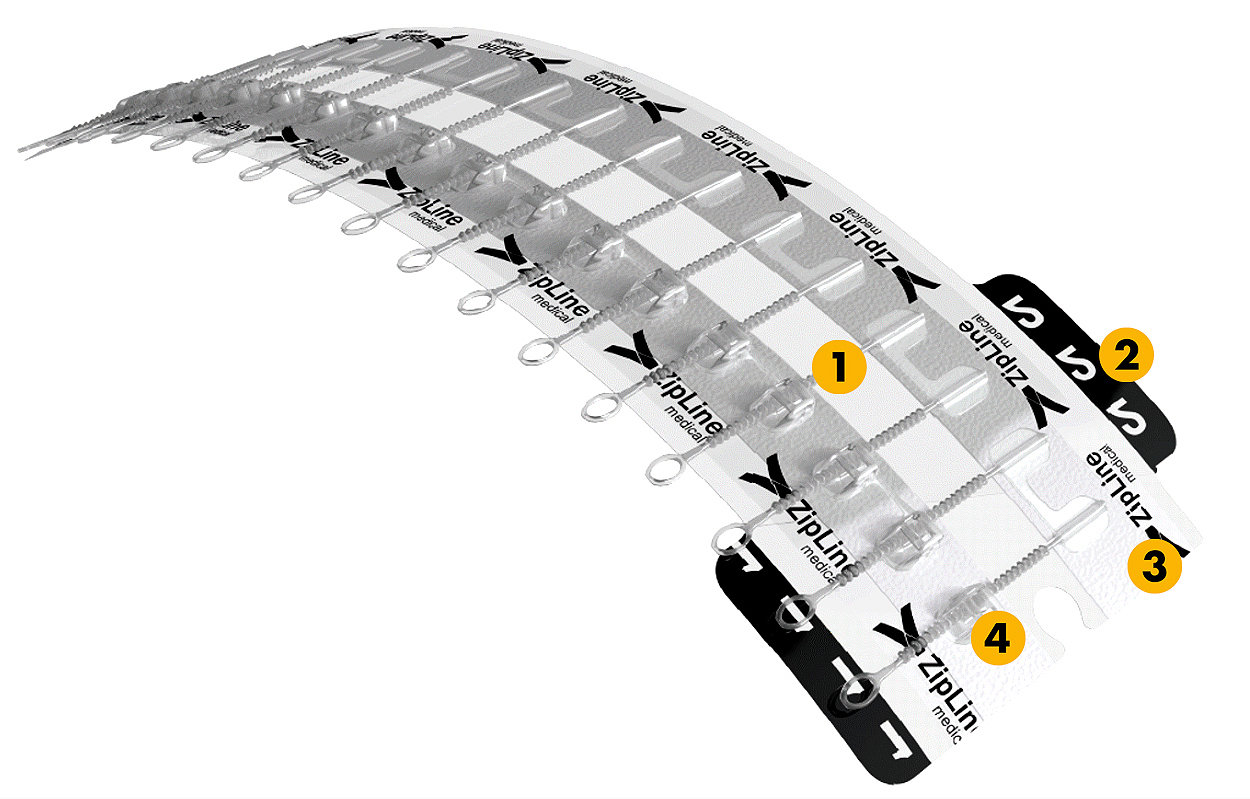

1. Isolation
The scaffold-like structure creates an isolation zone around the wound, designed to protect it from external forces.
2. Protection
Secure hydrocolloid adhesion designed to stick to the skin has shown to be 12x stronger2 than sutures.
3. Flexibility
Dynamic compression can maintain wound integrity while providing better flexibility.
4. Adjustability
Greater isolation from tension known to promote scarring.
is designed for...
Better outcomes
- Surgical sites have significantly less wound related complications post-operatively.1,2
- ZIP patients required less post-operative care for removal compared to staples.2,3
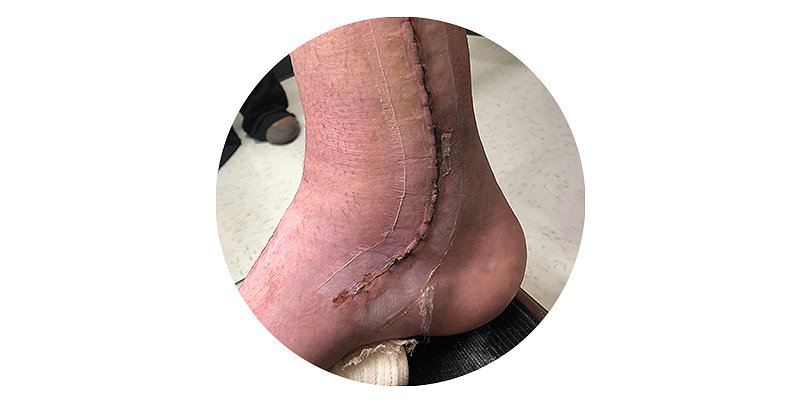
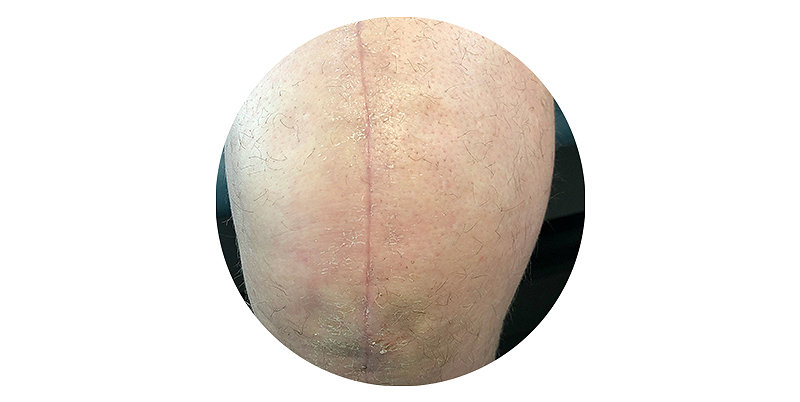
Superior scar quality
- Better cosmetic outcomes with no risk of needlestick injury3,4,5
- Hydrocolloid adhesive to allow for a puncture free closure
Faster closure
- Zip provides rapid, secure, adjustable closure6
- Zip is 4x faster than sutures7
- Suture closing time variability 8x higher than with Zip7
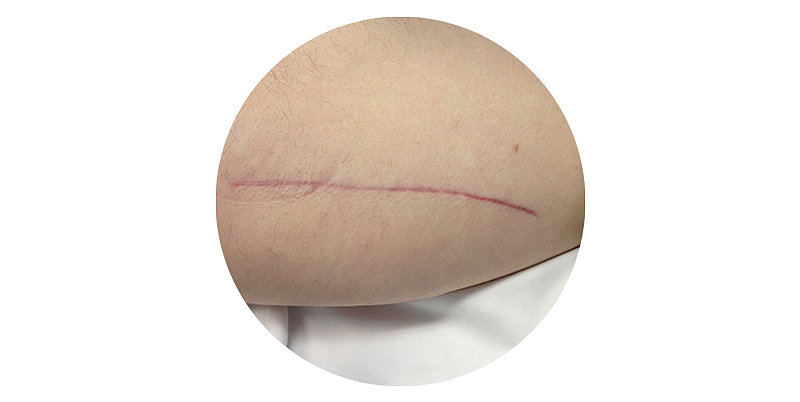
Stronger
than sutures8
Faster
than sutures7
cosmetic appearance4.
Designed to increase patient satisfaction3,5
Explore the data

''Do zip-type skin-closing devices show better wound status compared to conventional staple devices in total knee arthroplasty?''
''Using a non-invasive secure skin closure following total knee arthroplasty leads to fewer wound complications and no patient home care visits compared to surgical staples.''

''Patient Satisfaction and Cosmetic Outcome in a Randomized, Prospective Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty Skin Closure Comparing Zip Surgical Skin Closure with Staples.''
Zip
Skin Closure
· Fewer wound complications6
· Reduced scarring1
· Increased range of motion during recovery4
· No added pathways for bacteria
· Easier, faster, and less painful to apply and remove2,5

Contact us for more information on
Zip skin closure.
This information is intended solely for the use of healthcare professionals.
A healthcare professional must always rely on his or her own professional clinical judgment when deciding whether to use a particular product when treating a particular patient. Stryker does not dispense medical advice and recommends that healthcare professionals be appropriately trained in the use of any particular product before use.
The information presented is intended to demonstrate the breadth of Stryker product offerings. A healthcare professional must always refer to the package insert, product label and/or Instructions for Use before using any Stryker product. Products may not be available in all markets because product availability is subject to the regulatory and/or medical practices in individual markets. Please contact your Stryker representative if you have questions about the availability of Stryker products in your area.
Stryker Corporation or its divisions or other corporate affiliated entities own, use or have applied for the following trademarks or service marks: Stryker, Zip. All other trademarks are trademarks of their respective owners or holders.
References:
1. Alnachoukati O, Emerson R, Muraguri M (March 20,2019) Non-Invasive, Zip Type Skin Closure Device vs. Conventional Staples in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Which Method Holds Greater Potential for Bundled Payments?. Cures 11(3):e4281. DOI 10.7759/cureus.4281 - 2. Safa B, Belson A, Meschter C, et al. (August 04, 2018) In Vivo Efficacy Study Showing Comparative Advantage of Bacterial Infection Prevention with Zip-type Skin Closure Device vs. Subcuticular Sutures. Cureus 10(8): e3102. doi:10.7759/cureus.3102 - 3. Fillppa Linden Bergman, Anna Dahl, Christian Schllert, et. al., Non-invasive Zip wound-closure for lacerations in the adult and pediatric A&E, Department of Medicine and function of Emergency Medicine, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden; March 2019 Poster; Poster presented on March 13-15, 2019 at the Swedish Emergency Medicine Talks Conference in Stockholm, Sweden - 4. Tanaka Y, Miyamoto T, Naito Y, Yoshitake S, Sasahara A, Miyaji K. Randomized Study of a New Noninvasive Skin Closure Device for Use After Congenital Heart Operations. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016 Oct;102(4):1368-74. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.03.072. Epub 2016 Jun 1. PubMed PMID: 27261084 - 5. Ko, J. H., Yang, I. H., Ko, M. S., Kamolhuja, E. and Park, K. K. (2016), Do zip-type skin-closing devices show better wound status compared to conventional staple devices in total knee arthroplasty?. Int Wound J, 14: 250-254. doi:10.1111/iwj.12596 - 6. Menkowitz B, Olivieri G, Belson O (January 19, 2020) Patient Satisfaction and Cosmetic Outcome in a Randomized, Prospective Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty Skin Closure Comparing Zip Surgical Skin Closure with Staples. Cureus 12(1): e6705. DOI 10.7759/cureus.6705 - 7. Goldman DS, Hammill E, Aasbo J, Storne E, Reddy S. Improvement in S-ICD Incision Closure Time and High Implanter Satisfaction Using a Novel Skin Closure Device. Scientific presentation given at Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society 2017 Meeting; Sep 16, 2017; Yokohama, Japan. - 8. Levi K , et al. Mechanics of Wound Closure: Emerging Tape-Based Wound Closure Technology vs. Traditional Methods. Muacevic A, Adler JR, eds. Cureus. 2016;8(10):e827. doi:10.7759/cureus.827.
SMACC 2022-33314